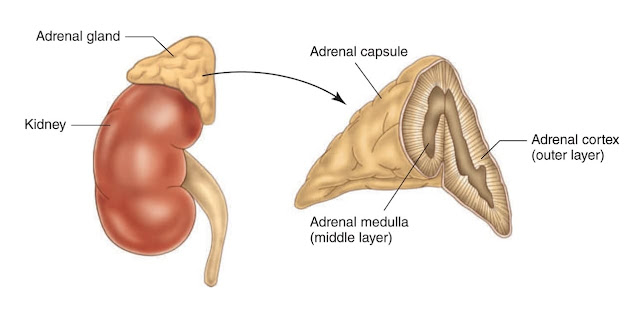
The adrenal glands, which are also known as the suprarenals, are so named because they are located with one on top of each kidney. Each of these glands consists of an outer portion, known as the adrenal cortex, and the middle portion, which is the adrenal medulla. Each of these parts has a specialized role.
 |
| Adrenal glands |
Functions of the Adrenal glands - one of the primary functions of the adrenal glands is to control electrolyte levels within the body.
 |
| Adrenal glands |
Other important functions of the adrenal glands include helping regulate metabolism and interacting with the sympathetic nervous system in response to stress.
Androgens are sex hormones secreted by the gonads, the adrenal cortex, and fat cells.
Corticosteroids are the steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex. The same term describes synthetically produced equivalents that are administered as medications.
More details: 📖 Grant’s Atlas of Anatomy 13th Edition
Adrenal Medulla
The adrenal medulla is embedded in the centre of the cortex of each adrenal gland. It is small, making up only about 10 percent of the total adrenal weight. The adrenal medulla is composed of chromaffin cells that are named for the granules within the cells that darken after exposure to chromium salts. These cells migrate to the adrenal medulla from the embryonic neural crest and represent specialized neural tissue. Indeed, the adrenal medulla is an integral part of the sympathetic nervous system, a major subdivision of the autonomic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system and the adrenal medulla are collectively known as the sympathoadrenal system. The chromaffin granules contain the hormones of the adrenal medulla, which include dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. When stimulated by sympathetic nerve impulses, the chromaffin granules are released from the cells and the hormones enter the circulation, a process known as exocytosis. Thus, the adrenal medulla is a neurohemal organ.
 |
| Anatomy and Physiology of the Adrenal Gland |
Adrenal Cortex
Cells of the adrenal cortex synthesize and secrete chemical derivatives (steroids) of cholesterol. While cholesterol can be synthesized in many body tissues, further modification into steroid hormones takes place only in the adrenal cortex and its embryological cousins, the ovaries and the testes. In adult humans the outer cortex comprises about 90 percent of each adrenal gland. It is composed of three structurally different concentric zones. From the outside in, they are the zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis.
The zona glomerulosa produces aldosterone, which acts on the kidneys to conserve salt and water. The inner two zones of the adrenal cortex—the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis—function as a physiological unit to produce cortisol and adrenal androgens (male hormones), with dehydroepiandrosterone, a weak androgen, being the major product. Cortisol has two primary actions: (1) stimulation of gluconeogenesis—i.e., the breakdown of protein and fat in muscle and their conversion to glucose in the liver—and (2) anti-inflammatory actions. Cortisol and synthetic derivatives of it, such as prednisone and dexamethasone, are known as glucocorticoids, so named because of their ability to stimulate gluconeogenesis. In severely stressed patients these compounds not only facilitate glucose production but also raise blood pressure and reduce inflammation. Because of their anti-inflammatory properties, they are often given to patients with inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and asthma. Glucocorticoids also reduce the function and action of the immune system, making them useful for protecting against transplant rejection and ameliorating autoimmune and allergic diseases.
Vascular anatomy
The suprarenal glands require a large supply of blood and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. The suprarenal glands are among the most extensively vascularized organs in the body. Three sources of arteries maintain blood supply to the suprarenal glands.
 |
| Adrenal glands - Vascular anatomy |
The superior suprarenal arteries are multiple small branches from the inferior phrenic artery, whereas the middle suprarenal artery is a direct branch from the abdominal aorta. An inferior suprarenal artery, sometimes multiple, arises from the renal artery on each side. After the suprarenal glands have been supplied with blood from these arteries, the blood drains through the suprarenal vein to the left renal vein or directly to the inferior vena cava on the right side.
References
1: Raharison F, Bourges Abella N, Sautet J, Deviers A, Mogicato G. Anatomy,
histology, and ultrasonography of the normal adrenal gland in brown lemur:
Eulemur fulvus. J Med Primatol. 2017 Apr;46(2):25-30. doi: 10.1111/jmp.12255.
Epub 2017 Feb 16. PMID: 28295350.
2: Coupland RE. The adrenal glands. Nurs Times. 1977 Nov 10;73(45):1748-51.
PMID: 928131.
3: Takahashi K, Shoji I, Shibasaki A, Kato I, Hiraishi K, Yamamoto H, Kaneko K,
Murakami O, Morimoto R, Satoh F, Ito S, Totsune K. Presence of kisspeptin-like
immunoreactivity in human adrenal glands and adrenal tumors. J Mol Neurosci.
2010 May;41(1):138-44. doi: 10.1007/s12031-009-9306-4. Epub 2009 Nov 7. PMID:
19898965.
4: Leoutsakos B, Leoutsakos A. The adrenal glands: a brief historical
perspective. Hormones (Athens). 2008 Oct-Dec;7(4):334-6. doi:
10.14310/horm.2002.1216. PMID: 19121996.
5: Erdoğan S, Pérez W. Arterial vascularization and morphological
characteristics of adrenal glands in the Pampas deer (Ozotoceros bezoarticus,
Linnaeus 1758). Anat Histol Embryol. 2014 Oct;43(5):369-74. doi:
10.1111/ahe.12085. Epub 2013 Sep 4. PMID: 24001368.
6: Sun N, Wu Y, Nanba K, Sbiera S, Kircher S, Kunzke T, Aichler M, Berezowska S,
Reibetanz J, Rainey WE, Fassnacht M, Walch A, Kroiss M. High-Resolution Tissue
Mass Spectrometry Imaging Reveals a Refined Functional Anatomy of the Human
Adult Adrenal Gland. Endocrinology. 2018 Mar 1;159(3):1511-1524. doi:
10.1210/en.2018-00064. PMID: 29385420; PMCID: PMC5839739.
7: Shady KL, Brown JJ. MR imaging of the adrenal glands. Magn Reson Imaging Clin
N Am. 1995 Feb;3(1):73-85. PMID: 7767747.
8: Cerny JC. Anatomy of the adrenal gland. Urol Clin North Am. 1977
Jun;4(2):169-77. PMID: 898413.
9: ANATOMY of the adrenal glands. Scope (Kalamazoo). 1945;(12):2. PMID:
21016659.
10: Pityński K, Skawina A, Polakiewicz J, Walocha J. Extraorganic vascular
system of adrenal glands in human fetuses. Ann Anat. 1998 Aug;180(4):361-8. doi:
10.1016/S0940-9602(98)80045-9. PMID: 9728279.




No comments:
Post a Comment