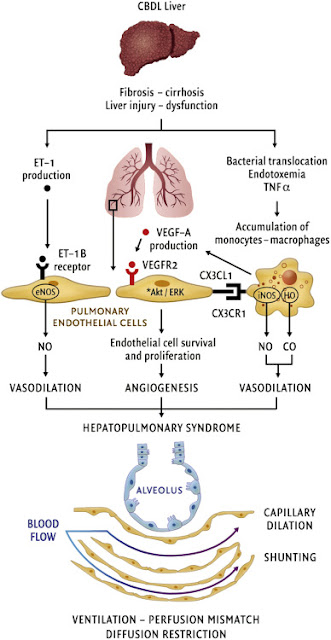
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is defined as a clinical disorder (associated with advanced liver disease) due to disturbed pulmonary gas exchange leading to hypoxemia and widespread intrapulmonary vasodilation and shunting of blood in the absence of detectable primary cardiopulmonary disease.
 |
| Hepatopulmonary syndrom |
In chronic liver disease, pulmonary affection is common and may result in hypoxia and cyanosis. The pulmonary changes that may complicate chronic liver diseases are:
•• Hypoxia.
•• Intrapulmonary shunting of blood via microscopic AV fistula (from pulmonary arteriole to vein).
•• Reduce transfer factor—due to deposition of collagen in the vessel wall causing thickening of vessel wall resulted in reduced gas exchange.
•• Pleural effusion.
•• Raised diaphragm.
•• Basal atelectasis.
•• Primary pulmonary hypertension.
The syndrome is characterized by:
•• Platypnea (dyspnea in sitting posture).
•• Orthodeoxia (reduced O2 saturation in sitting and standing posture than supine posture).
•• Cyanosis.
•• Spider nevi and clubbing (inconstant finding).
The disease is mostly found with autoimmune hepatitis or long-standing cirrhosis.
 |
PATHOLOGY/PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The Aa-PaO2 gradient exceeds 15 mm Hg. The intrapulmonary shunting is via microscopic arteriovenous (AV) fistula. The vasoactive substances that could involve in pulmonary vasodilatation are unknown probably NO, endothelin and other arachidonic acid metabolites are responsible for pulmonary vasodilation and shunting.
DIAGNOSIS
•• Increase Aa-Pa gradient O2 > 15 mm Hg.
•• Transthoracic contrast enhanced echocardiography.
•• 99mmTc macroaggregated albumin lung scan.
•• Pulmonary angiography—Spongy appearance of basal pulmonary vessels correspond to the infiltrate in lung field.
MANAGEMENT
•• No pharmacological treatment is effective.
•• Hepatic transplantation is the best mode of therapy.
•• Reversal is not always guaranteed where AV shunts are large. Then they require coil embolic therapy which should precede transplant.
•• TIPS—It can be useful for palliation in a patient awaiting for hepatic transplantation.
References
Tags: hepatopulmonary syndrome, hepatopulmonary syndrome treatment, hepatopulmonary syndrome radiology, hepatopulmonary syndrome symptoms, hepatopulmonary syndrome triad, hepatopulmonary syndrome diagnosis, hepatopulmonary syndrome pathophysiology, hepatopulmonary syndrome uptodate, hepatopulmonary syndrome mortality, hepatopulmonary syndrome anesthesia, hepatopulmonary syndrome and portopulmonary hypertension, hepatopulmonary syndrome amboss, hepatopulmonary syndrome aasld, hepatopulmonary syndrome abg, hepatopulmonary syndrome after liver transplantation, hepatopulmonary syndrome and pulmonary hypertension, hepatopulmonary syndrome and liver transplant, hepatopulmonary syndrome bubble study, hepatopulmonary syndrome bubble echo, hepatopulmonary syndrome bubble, hepatopulmonary syndrome breathing


No comments:
Post a Comment