The eyes appear driven downward in this infant with hydrocephalus.
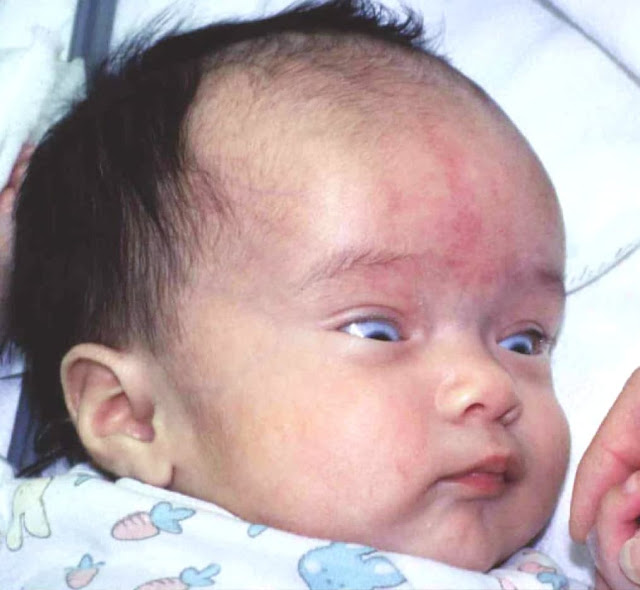 |
| Setting-Sun Phenomenon |
The setting-sun phenomenon is an ophthalmologic sign in young children resulting from upward-gaze paresis. In this condition, the eyes appear driven downward, the sclera may be seen between the upper eyelid and the iris, and part of the lower pupil may be covered by the lower eyelid. Pathogenesis of this sign is not well understood, but it seems to be related to aqueductal distention with compression of periaqueductal structures secondary to increased intracranial pressure.
More details: 📖 Merritt’s Neurology Handbook 10th Edition
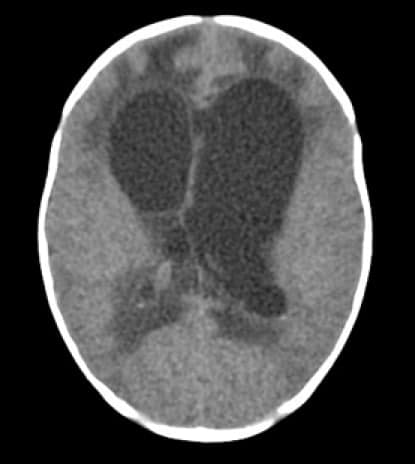 |
| CT scan, showing marked hydrocephalus in infant with setting-sun eye phenomenon |
References
1975 Aug;17(4):447-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1975.tb03496.x. PMID: 1158051.
2: Boragina M, Cohen E. An infant with the "setting-sun" eye phenomenon. CMAJ.
2006 Oct 10;175(8):878. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.060507. PMID: 17030938; PMCID:
PMC1586074.
3: Yoshikawa H. Benign "setting sun" phenomenon in full-term infants. J Child
Neurol. 2003 Jun;18(6):424-5. doi: 10.1177/08830738030180061601. PMID: 12886979.
4: Haverkamp F, Weimann E. Familial benign setting-sun phenomenon in healthy
newborns. Clin Genet. 1995 Mar;47(3):167. doi:
10.1111/j.1399-0004.1995.tb03953.x. PMID: 7634542.
5: STILLHART H. Uber die klinische Bedeutung des sogenannten reflexartigen
Phänomens der untergehenden Sonne beim Neugeborenen [The clinical significance
of the so-called setting sun reflex phenomenon in the newborn]. Helv Paediatr
Acta. 1954 Oct;9(4):298-310. German. PMID: 13221165.
6: Können GP, van der Werf SY. Reflection halo twins: subsun and supersun. Appl
Opt. 2011 Oct 1;50(28):F80-8. doi: 10.1364/AO.50.000F80. PMID: 22016250.
No comments:
Post a Comment