The affected veins in the superficial venous system are pulled out through small incisions in the skin (stripped). This procedure is also known as "Babcock's procedure" or "Babcock's stripping". The American doctor Babcock described the method for the first time in 1907. This classic method is used to remove the affected segments of the worst affected long saphenous vein that runs from the ankle up to the inguinal fold.
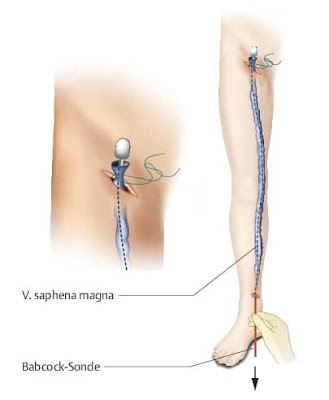 |
| Babcock's operation |
The saphenous vein can only be removed, if the deep venous system is healthy. This is first checked by an ultrasound examination (Doppler ultrasonography), sometimes also with contrast medium X-rays (phlebography). Several days before the procedure, patients should not drink any alcohol or take medicines that delay blood clotting. These include most painkillers.
📖 Clinical Surgery: With Student Consult Access
After the procedure, the incisions are closed and a compression dressing wrapped tightly around the leg. Anti-embolism garments, such as mediven struva.
After vein stripping
After the procedure, patients must wearing compression stockings for at least three months. They should also avoid long periods of standing or sitting. During a series of follow-up examinations, the doctor checks the course of healing and the treatment outcome. Vein stripping is considered a very safe method for treating varicose veins. Possible side effects of the procedure, which usually disappear after a short time or can be prevented by compression stockings.
Professor William Wayne Babcock (1872-1963)
 |
| William Wayne Babcock |
Professor William Wayne Babcock (1872-1963) is considered as a leading figure of American surgery during early 20th century. He introduced many innovative surgical techniques such as Babcock operation for the treatment of varicose veins, the Babcock-Bacon operation for the treatment of cancer of the rectum and sigmoid colon preserving anal sphincters, the “soup bone” cranioplasty technique, and the nerve disassociation technique for the relief of certain forms of paralysis or parasthesia due to injury or inflammation. He invented many surgical instruments such as Babcock forceps, which is widely used in everyday surgical practice, the Babcock probe, and also sump drain and lamp chimney sump drain, which also bear his name. In 1947, he received the Master Surgeon Award from the International College of Physicians and Surgeons and in 1954 the American Medical Association presented him with the Distinguished Service Medal.
References
No comments:
Post a Comment